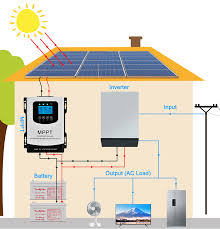
Solar charge controller
A solar charge controller is a critical component in off-grid and hybrid solar systems, regulating the power flow between solar panels, batteries, and loads to prevent overcharging and battery damage. It ensures efficient energy storage and prolongs battery life.
Types of Solar Charge Controllers:
-
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) – Budget-friendly, suitable for small systems.
-
MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) – More efficient (up to 30% better), ideal for larger systems.
Key Features & Benefits:
✔ Battery Protection – Prevents overcharging & deep discharge.
✔ Load Control – Manages DC appliances (optional in some models).
✔ LCD/Bluetooth Monitoring – Displays voltage, current & charging status.
✔ Wide Compatibility – Works with lead-acid, LiFePO4, and gel batteries.
✔ Auto Voltage Detection – 12V/24V/48V support.
Applications:
-
Off-grid solar systems (homes, cabins, RVs)
-
Street lighting & solar water pumps
-
Battery backup systems
Solar Charge Controller: The Guardian of Your Off-Grid Power System
A Solar Charge Controller (also known as a solar regulator) is an essential electronic device that acts as the gatekeeper and guardian between a solar panel array and a battery bank. Its primary, critical function is to regulate the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to safely and efficiently charge the batteries, preventing overcharging and damage.
Core Purpose: Why It’s Indispensable
Batteries require a specific charging profile (voltage and current levels) to reach full capacity without being harmed. Solar panels, however, can produce variable and often excessive voltage, especially on cold, sunny days. Without a controller, this overvoltage would severely overcharge the batteries, causing:
-
Electrolyte loss (in flooded lead-acid)
-
Internal heating and swelling
-
Permanent capacity loss
-
Significantly reduced lifespan
-
Potential fire or safety hazards
Conversely, a charge controller also prevents reverse current flow at night, stopping batteries from discharging back through the solar panels.
Key Types and Technologies:
There are two main types, defined by their charging methodology:
-
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation):
-
Function: Essentially acts as a switch that connects the solar array directly to the battery. It rapidly pulses (turns on and off) to maintain the battery at the correct voltage.
-
Best For: Smaller systems where the solar panel voltage closely matches the battery bank voltage (e.g., 12V panel to 12V battery). A cost-effective and reliable solution for basic applications.
-
-
MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking):
-
Function: A more advanced, intelligent regulator. It operates like a “smart DC-to-DC converter.” It continuously tracks the panel’s Maximum Power Point (Vmp) to harvest the absolute maximum available power, then transforms that higher voltage down to the precise voltage required by the battery, while increasing the output current.
-
Key Advantage: Significantly higher efficiency gains (typically 15-30% more energy harvest compared to PWM), especially in cold weather or when panel voltage is much higher than battery voltage (e.g., connecting a large 60V panel array to a 24V battery bank).
-
Best For: Virtually all modern systems where maximizing energy yield and return on investment is critical. Essential for larger residential, commercial, and off-grid systems.
-
Essential Features and Protections:
Modern charge controllers offer a suite of intelligent features:
-
Multi-Stage Charging: (Bulk, Absorption, Float) Optimizes battery health and lifespan by applying the correct voltage for each stage of the charge cycle.
-
Load Control: Many have programmable outputs to directly power DC loads (like lights) with low-voltage disconnect (LVD) to prevent over-discharging the battery.
-
Comprehensive Protections: Overcharge, over-discharge, short-circuit, reverse polarity, and over-temperature protection.
-
Communication & Monitoring: Advanced models offer Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or data logging to monitor system performance via a smartphone app or computer.
-
Battery Compatibility: Programmable settings for various battery types: Flooded Lead-Acid, AGM, Gel, and Lithium (LiFePO4).
Choosing the Right Controller:
Selection depends on three key factors:
-
System Voltage: (e.g., 12V, 24V, 48V).
-
Maximum Solar Array Current: The controller’s current rating (in Amps) must exceed the total short-circuit current (
Isc) of the panel array. -
Solar Array Maximum Power Voltage (Vmp): For MPPT controllers, the input voltage (
Vmpat coldest temperature) must be within the controller’s specified range.
Conclusion:
The solar charge controller is a non-negotiable component for any system with battery storage. It is the critical piece of intelligence that ensures batteries are charged efficiently, protected from damage, and given a long, productive life.
For More Details Contact us on 0304-1111-988
Also Follow our Facebook Page